Abstract
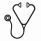
Background. Polycythemia (PV) patients with hematocrit above 45% are at increased risk of thrombotic complications and are treated with phlebotomy and/or cytoreductive therapy to reach a hematocrit target below 45%. Rusfertide (PTG-300) is a peptidic mimetic of hepcidin that is being developed for treatment of polycythemia vera (PV). A Phase 2 trial has indicated that rusfertide is effective at reducing the number of phlebotomies and maintaining hematocrit below 45% without phlebotomy in PV patients who are either high-risk or low-risk, patients treated with cytoreductive therapy (hydroxyurea, interferon, ruxolitinib) and patients treated with phlebotomy alone (Kremyanskaya, ASH 2020). The current trial (PTG-300-08) tested the ability of rusfertide to normalize hematocrit in PV patients with elevated hematocrit without instituting phlebotomy treatment to normalize hematocrit to below 45% in PV patients without requiring phlebotomy and/or cytoreductive treatment.
Methods. Eligible study subjects were diagnosed with PV (in accordance with the WHO 2016 criteria), had baseline hematocrit above 48%, and a history of 3 or more hematocrit values above 48% in the year prior to enrollment. High-risk and low-risk subjects treated with phlebotomy alone or with concurrent cytoreductive therapy were eligible. Rusfertide was added on to each subject's current therapy. The initial rusfertide dose was 40 mg administered subcutaneously twice weekly. When each subject's hematocrit was below 45%, the dosing schedule was changed to weekly and the rusfertide dose was adjusted to maintain hematocrit below 45%.
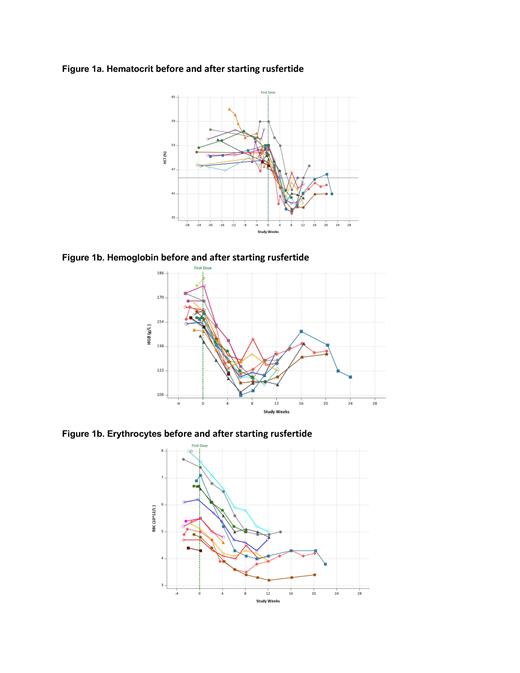
Results. Sixteen subjects (12 male and 4 females) have been enrolled. The mean age is 56.1 years; the mean time since diagnosis is 3.74 years; 10 subjects are low risk PV; 12 subjects are receiving concurrent hydroxyurea and 4 subjects were not receiving cytoreductive therapy. Baseline values (mean, min-max) HCT (51.0%, 47.4 - 59), WBC (12,338/µL, 7,000 - 24,600), RBCs (5.9x10 6/µL, 4.3 - 7.6), platelets (486,500/µL, 242,000 - 904,000). All subjects had rapid decreases in hematocrit to below 45% without the use of phlebotomy (Figure 1a). Hematocrit levels remained well controlled after falling below 45% as investigators reduced rusfertide dose to maintenance once weekly regimen. Hemoglobin (Figure 1b) fell rapidly. Erythrocyte counts (Figure 1c) also fell rapidly, indicating that decreased hematocrit is due to decreased erythrocytosis. For the 11 subjects with adequate follow-up, the mean rate of absolute hematocrit decrease was 1.76% per week (median: 1.81%/week; min - max: 0.65 - 2.69%) and the mean time to reach goal hematocrit below 45% was 4.79 weeks (median: 4.14 weeks, min - max: 3.57 - 8.14).
Eight subjects reported adverse events (AEs). Injection site reactions (ISRs) occurred in 7 subjects and were mild or moderate in severity. The most common ISRs were erythema (n=7), induration (n=5) and pruritis (n=2). Adverse events other than ISRs that occurred in 2 or more subjects were hypertension (n=2), pyrexia (n=2) and thrombocytosis (n=2). There were two serious adverse events (worsening migraine and pleuritic chest pain) and both were considered unrelated to rusfertide. Overall, rusfertide was well tolerated.
Conclusions. This study demonstrates that induction therapy with twice weekly rusfertide administration was effective in rapidly achieving target hematocrit below 45% without phlebotomy in all PV patients which was then successfully maintained with weekly rusfertide treatment. Moreover, the twice weekly injections of rusfertide used to rapidly lower hematocrit levels were safe and well tolerated.
Key words: Hepcidin, Hematocrit, Rusfertide, PTG-300, Polycythemia Vera, PV, Therapeutic Phlebotomy
Gupta: Protagonist Therapeutics: Current Employment. Valone: Protagonist Therapeutics: Consultancy, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Khanna: Protagonist: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Modi: Protagonist Therapeutics: Current Employment. Hoffman: Kartos Therapeutics, Inc.: Research Funding; Protagonist Therapeutics, Inc.: Consultancy; Novartis: Other: Data Safety Monitoring Board, Research Funding; AbbVie Inc.: Other: Data Safety Monitoring Board, Research Funding.
Author notes
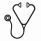 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract